Access to and Use of Electronic Journal for Research by Postgraduate Students in Two Universities in Oyo State, Nigeria
Keywords:
Universities, Electronic journals, Postgraduate students, ResearchAbstract
There is a preponderance of electronic information resources, especially journals for academic pursuits. The study aims at investigating the access to and use of electronic journals among postgraduate students. A quantitative research approach was adopted for the study using a survey as a research method. Postgraduate students of the University of Ibadan and Ladoke Akintola University of Technology (LAUTECH), Ogbomosho, were used as respondents in the study. Four research questions guided the study. A sampling fraction of 40% was used to select a sample of 384 postgraduate students. A questionnaire was used to collect data. Thus, 384 copies of the questionnaire were administered and 384 were retrieved and found useable for data analysis. This represents a response rate of 100.0%. Findings showed that the awareness level of electronic journals for research among postgraduate students was above average. Most of the respondents also agreed that electronic journals were readily accessible for research. It was also found that many of the respondents used e-journals more occasionally, monthly, and weekly while the majority of them never used some of these journals. Based on the findings, it was concluded that constant accessibility will influence the positive use of electronic journals for research by postgraduate students.
Keyword: Universities, Electronic journals, Postgraduate students, Research
Introduction
Journals are important resource vehicle for global scholarly communication. Singh & Bebi (2012) stated that journals play a role in the research and development activities and undisputedly are considered primary channels of information dissemination. However, sweeping changes in information communication technologies (ICTs) in recent years have given an amazing boost to electronic publishing. This event marked the paradigm shift in scholarly communication, from printed journals as the principal medium of communication to electronic journals.
Boakye, Martin-Yeboah, & Fynn (2015) describe e-journals as publications issued in successive order that are available in digital format. An electronic journal as defined by Panda & Mohanta (2008) is any journal, magazine, newsletter, or serial publication available over the Internet in electronic format. E-journals are global information highways and are being added to library collections at exponential rates. Libraries are doing extensive work to make e-journals available to their users and keeping them abreast of the latest developments in their field of interest (Vasishta & Naviiyoti, 2011). Electronic journals are grouped as online journals and off-line journals. Online journals are paid e-journals that are available on ‘cost-per-access’ bases via online databases while offline journals are journals published on CD-ROMs or other media that do not require Internet access (Salau & Gama, 2015).
According to Cook & Jones (2000), electronic journals are provided to subscribers through the following types of the medium which include free access, exclusive subscription, selective access, fee-based access, and consortium-based access. They also stated that e-journals were predominately distributed through subscription from the publishers or through aggregator databases. Subscriptions through publishers were made either through vendors or directly from e-journal publisher’s websites.
Madondo, Sithole, & Chisita (2017) stated that the advantages of e-resources include access to information that might be restricted to the user due to geographical location or finances, access to more current information, and provision of extensive links to additional resources related to content. In a similar view, Maxymuk (2014) acknowledged that the advantages of electronic journals include no physical space required and accessibility from almost any work station that can be connected remotely to an institution network. Because of this, Chirra & Madhusudhan (2009) noted that the demand for electronic journals (e-journals) among the academic and research community has increased over the years. E-journals are fast gaining wider acceptability and usage as most researchers and scholars now made their research findings available through electronic journals (Aladeniyi, 2017).
With the emergence of the digital age and electronic resources, access to information is relatively enhanced as information is made available and accessible to academic staff through computers, the Internet, digital libraries, and related electronic networks, and is readily used in the research process. Thus, in the emerging electronic information environments in Nigerian universities, electronic resources now provide platforms for accessibility and utilization of information in the research process, as they are perceived to have a positive effect on research productivity (Ani, Nguluba & Onyancha 2015).
Shuling (2007) reveals that electronic information has steadily become a key resource in every university library. The development of e-resources has rapidly transformed information access and management procedures in the academic environment and particularly in university libraries. Through the use of e-resources, students, researchers, and other information seekers are now exposed to various accesses to electronic information resources globally. However, in recent decades, the majority of researchers and academicians particularly in the developing countries have been deprived of access to key research literature found mainly inexpensive journals published in developing countries. This situation is due to a reduced library budget which could not cope with the enormous journal subscription cost and inadequate distribution mechanism (Rosenberg & Raseroka, 2000; Rao, 2001; Moahi, 2002; Lwoga, Chimwaza, Aronson &Vent 2007).
It is pertinent to note that when postgraduate students are aware of e-resources, they make adequate use of them for academic and research purposes. It is also important to note that for the students to make use of the e-resources, they ought to be skilled in information and communication technologies (ICTs) applications to gain independent use of various electronic information resources around the globe. Be that as it may, it has been observed that postgraduate students in Nigerian universities are confronted with various challenges relating to inadequate telecommunications’ infrastructure, high cost of the subscription, poor user skills, amongst others in the use of e-resources (Akpojotor, 2016).
Statement of the Problem
In recent years, postgraduate students face pressure like an increase in tuition fees, increased accommodation charges, the rising cost for e-book purchases, and the cost incurred in carrying out research projects. Research writing is very important and compulsory for postgraduate students in Nigeria. Quality research project to a large extent requires quality, quantity, and relevance of resources consulted and cited (Bofong, 2003). The use of Internet/electronic journals could be maximized by postgraduate researchers through access to the relevant and large number of information resources globally. Adomi, Okiy, & Ruteyan (2003), Jagboro (2003), Oduwole, & Akpati (2003) in their various studies identified the high use of electronic information resources among Nigeria students. Research is the bane of postgraduate studies. Despite the availability of these resources and their benefits to university education, their effective uses by postgraduate students are being hampered by varying factors. Given the foregoing, this study examined the access to and use of electronic journals for research by postgraduate students in two selected universities in Oyo State, Nigeria.
Objectives of the study
The general objective of the study is to examine the postgraduate students’ access to and use of electronic journals for research in two selected universities in Oyo State, Nigeria. The specific objectives of this study are to:
i) determine the level of awareness of electronic journals by postgraduate students;
ii) determine the level of accessibility to electronic journals by postgraduate students;
iii) determine the frequency of use of electronic journals by postgraduate students;
iv) identify the problems encountered by postgraduate students in the use of electronic journals.
Research Questions
i) What is the level of awareness of electronic journals by postgraduate students?
ii) What is the level of accessibility to electronic journals by postgraduate students?
iii) What is the frequency of use of electronic journals by postgraduate students?
iv) What are the problems encountered by postgraduate students in the use of e-journals?
Literature review
Works of literature were reviewed in line with the research questions
Awareness of Electronic Journals by Postgraduate Students
Awareness is paramount if postgraduate students are to effectively and efficiently use electronic resources. (Akpojotor, 2016). Similarly, Katabalwa & Underwood (2017) noted that awareness of available electronic journals plays a key role when it comes to accessing and using these resources. Asemi & Riyahiniya (2007) concluded that awareness of the existing library electronic resources is crucial in influencing usage of the resources and maintained that when a user is aware of resources it would usually lead to greater use of those resources. Chirra & Madhusudhan (2009) in a survey on the use of electronic journals by doctoral research scholars of Goa University, India, revealed that all (100%) of respondents were aware of the e-journals of the Consortium and accessed them.
Accessibility of Electronic Journals by Postgraduate Students
Information that is available but not accessible to postgraduate students for research is of no value. Okoye & Ejikeme (2011) affirmed the necessity of accessing needed information research, in enriching education and sharing of knowledge; since there is a critical need to make research results available to as many academics and elite class as possible. Shuling (2007) reveals that electronic information has steadily become a key resource in every university library. Tobia & Hunnicult (2008) posit that electronic journals have become the preferred method for accessing the journal literature.
Kling & Callahan (2003) indicated that scholars highly value e-journals access and most of the scholars preferred e-journals overprint mostly for the following reasons: e-journals save time, make work easier, resulting in better quality research, and enable the scholar to find more materials. Both Israel & Edesiri (2017) and Naick & Bachalla (2016) agreed with each other in their position that, e-resources facilitate access to relevant and current information for learning and research development.
Use of Electronic Journals by Postgraduate Students
Recent studies on the use of e-journals suggested that e-journals constitute an important source of information and that it is one of the most frequently used resources, especially among postgraduate students. Otu, Asante, & Martin (2015) noted that one of the most frequently used resources is electronic journals.
The study conducted by Bansode (2013) revealed that out of 264 respondents, 131 (49.63%) respondents make use of electronic journals 2/3 in a week and that the major category of the respondents comprises of research scholars, followed by post-graduate student and faculties. It was reported in the study that 69 (26.14%) faculties are using electronic journals for various reasons such as keeping themselves updated with the new information appearing in their subject of interest and preparing for the lecture and also carrying out their research.
Challenges with Access and Utilisation of Electronic Journals by Postgraduate Students
Various studies have reported several challenges regarding access to and use of electronic journals for research. Ajegbomogun (2007) observed that while electronic journals have become essential tools for learning, teaching, and research, most of the scholars and researchers are not fully utilising them. The findings of a study conducted by Madhunsudhan (2010) involving 60 research scholars at Kurukshetra University; New Delhi also revealed a lack of proper IT skills, slow internet connectivity, and difficulty in getting relevant information as hindrances to using electronic resources.
Also, a study carried out by Anhwere & Paulina (2018) reported that three major factors that affect postgraduate student’s inability to use electronic resources were poor internet connectivity, power outages, and inadequate internet. Other challenges include high cost of access and usage of online resources, non-subscription for relevant online resources by institutions; and lack of sponsored training from the institutions (Agber & Agwu, 2013)
Research Methodology
A quantitative research approach was adopted for the study, using a survey as a research method. Postgraduate students of two selected universities in Oyo State,, the University of Ibadan and Ladoke Akintola University of Technology (LAUTECH), Ogbomosho, were used as respondents in the study. Three faculties were purposively selected with the highest number of postgraduate students in LAUTECH and the same faculties were also selected in the University of Ibadan for ease of comparison. The selected faculties were Faculties of Engineering/Technology, Agriculture/Forestry, and Science. The purposive selection of two departments in each faculty with the highest number of postgraduate students was done, while the proportionate random sampling technique was used to select postgraduate students. The selected scholarly journals used for the study are the most widely used electronic journals in the Sciences, Agriculture/Forestry, and Engineering respectively.
A sampling fraction of 40% was used to select a sample of 384 postgraduate students. The questionnaire was used to collect data. Thus, 384 copies of the questionnaire were administered and 384 were retrieved and were found useable for data analysis. This represents a response rate of 100.0%. A simple per cent statistical tool was used to answer the research questions.
Data Analysis and Discussion of Findings
Data were analyzed and results were presented in line with the study research questions
Research Question One: What is the level of awareness of electronic journals by postgraduate students?
Table 1: Level of Awareness of E-Journals for Research by Postgraduate Students
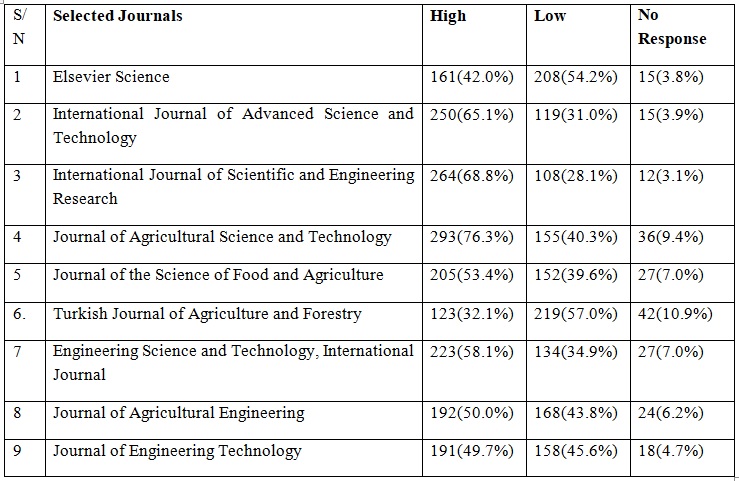
As shown in Table 1, 293(76.3%) of the respondents indicated high level of awareness of Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, while 155(4.3%) indicated a low level of awareness of Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology and 36(9.4%) of the respondents gave no response which indicated they were not aware of Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology. As far as International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research is concerned, 264(68.8%) of the respondents indicated a high level of awareness of the journal while 108(28.1%) indicated a low level of awareness of International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research and only 12 (3.1&) respondents gave no response. For the International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology, 250(65.1%) indicated they had a high level of awareness of the journal while 119(31.0%) indicated they had low awareness of the journal and 15(3.9%) gave no response. However, 219(57.0%) of the respondents sampled indicated a low level of awareness of the Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry while 123(32.1%) indicated a high level of awareness of the journal and 42(10.9%) respondents gave no response. Likewise, for Elsevier Science journals, 208(54.2%) of the respondents indicated a low level of awareness of the journal while 161(42.0%) of the respondents indicated high-level awareness of the journal and 15(3.8%) of the respondents gave no response. Furthermore, 168(43.8%) of the respondents indicated low-level awareness of the Journal of Agricultural Engineering, while 192(50.0%) indicate a high level of awareness of the journal and 24(6.2%) of the respondents gave no response.
It was observed from the result of the findings in this study that postgraduate students had more than 50% level of awareness of different kinds of electronic journals for research. The findings of the study are in line with Agyekum & Ossom (2015) who observed that most of the users are aware of e-journals and that they are not only using them for building and updating their knowledge but also for collecting relevant materials for their study and research purpose as information can be acquired expeditiously.
Research Question Two: What is the level of accessibility to electronic journals by postgraduate students?
Table 2: Level of Accessibility of E-Journals for Research by Postgraduate Students
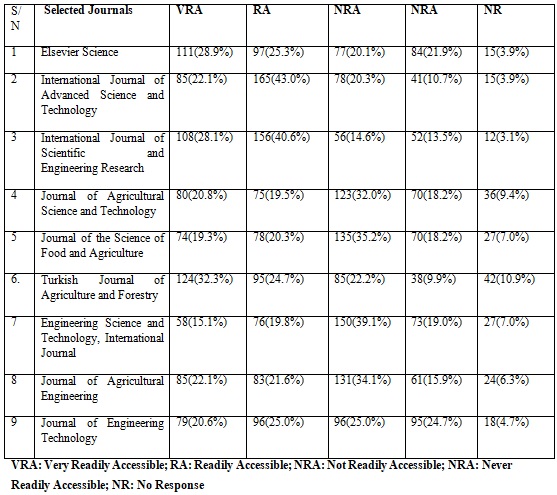
As shown in Table 2, 264(68.7%) indicated that the International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research was accessible to them while 108(28.1%) indicated that the International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research was not accessible to them. Also, 250(65.1%) of the respondents sampled indicated that the International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology was accessible to them while 119(31.0%) of the respondents were not accessible to them. 219(57.0%) of the respondents sampled indicated that the Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry was accessible to them while 123(32.1%) of the respondents indicated that the Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry was not accessible to them. However, 223(58.1%) of the respondents indicated that Engineering Science and Technology, International Journal was accessible to them while 134(34.9%) of the respondents indicated that Engineering Science and Technology, International Journal was not accessible to them. Also, 205(53.4%) of the sampled respondents indicated that the Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture was not accessible to them while 152(39.6%) of the respondents indicated that the Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture were readily accessible to them. Furthermore, 193(50.2%) of the respondents indicated that the Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology was not accessible to them while 155(40.3%) indicated the Journal of the Science of food and Agriculture was accessible to them.
From the findings, the accessibility among respondents was higher for International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research, 264(68.7%), International Journal of Advanced Science250 (65.1%), Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry 219 (57.0%), Elsevier Science208 (54.2%) However, not very easily accessible were higher among respondents for Engineering Science and Technology, International Journal 223(58.1%), Journal of the Science of food and Agriculture 205(53.4%), Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology 193(52.2%), Journal of Agricultural Engineering 192 (50%) and Journal of Engineering Technology 191(49.7%). Hence, the level of accessibility of e-journals among the respondents for research is moderate.
Research Question Three: What is the frequency of use of electronic journals by postgraduate students?
Table 3: Frequency of E-Journals Usage for Research by Postgraduate Students
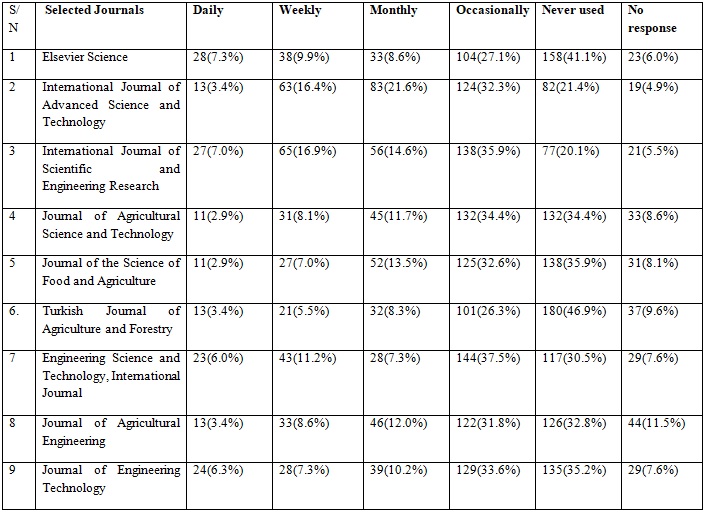
Findings in Table 3 showed that 28(7.3%) used Elsevier Science Journal daily, 65(16.9%) use International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research weekly, 83(21.6%) use International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology monthly, 144(37.5%) use Engineering Science and Technology, International Journal occasionally while 180(46.9%)of the respondents have never used Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry From the findings of the study, it is obvious that postgraduate students used electronic journals but the level of usage is not impressive. However, the preference of certain electronic journals over others affected usage because users tended to use certain e-journals that are tailored towards their research needs or discipline and ignored others that could be seen as not relevant.
Research Question Four: What are the problems encountered by postgraduate students in the use of e-journals?
Table 4: Problems encountered by postgraduate students in using E-Journals for Research
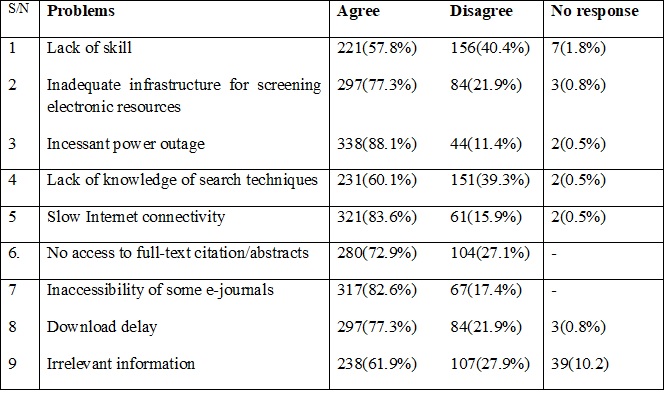
Table 4 above presents the information on the problems encountered by postgraduate students in the use of e-journals. It showed that “Incessant power outage” 338(88.1%) ranked highest as the major problem associated with electronic database use and was followed in succession by “Slow internet connectivity 321(83.6%), “Inaccessibility of some e-journals” 317(82.6%), “Inadequate infrastructure for screening electronic resources and Download delay” 297(77.3%) “No access to full-text citation/abstracts” 280(72.9%), “Irrelevant information” 238(61.9%), “Lack of knowledge of search techniques” 231(60.1%) “Lack of skill” 221(57.8%). This finding is supported by Anhwere & Paulina (2018) which reported that three major factors that affect postgraduate student’s inability to use electronic resources were poor Internet connectivity, power outages, and inadequate Internet.
Summary of Findings
This study examined postgraduate students’ access to and use of electronic journals for research in two selected universities in Oyo state. The major findings of the study are summarised as follows:
- postgraduate students were aware of the use of electronic journals for research. Their awareness level of electronic journals was above average.
- For each of the electronic journals assessed in this study, the majority of the respondents agreed that they were readily accessible for postgraduate use for research; hence, the level of accessibility of e-journals for research was moderate.
- many of the respondents used e-journals more occasionally, monthly, and weekly, while more of them never used some of these journals. Among the e-journals never used most were the Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry and Elsevier Science journals.
- some problems encountered by postgraduate students in the use of electronic journals for research. Top most among them are incessant power outage, slow Internet connectivity, and inaccessibility to some electronic journals.
Conclusion
Electronic journals are invaluable tools for research as they provide access to current and up to date information in different subject disciplines. Postgraduate students by their programme, engage in research to meet up with the academic requirements for the award of postgraduate degrees. Despite the importance of electronic journals in postgraduate research, previous researchers indicated that postgraduates faced challenges that hinder the accessibility and use of electronic journals for research.
Constant accessibility will influence the positive use of electronic journals for research by postgraduate students. Infrastructure to support electronic resource use and access such as electricity supply, computers, and their accessories, adequate bandwidth subscription, and technical assistance to uses should be put in place. It is needful for postgraduates to acquire needed skills and knowledge to utilize e-journals for research and Internet connectivity needs to be enhanced to improve download.
References
Adomi, E. E., Okiy, R. B., & Ruteyan, J .O. (2003). A survey of cybercafés in Delta State, Nigeria. The Electronic Library Journal, 21 (5), 487-495.
Agber, T. & Agwu E.A. (2013). Assessment of online resources usage by agricultural science lecturers of tertiary institutions in Benue State, Nigeria. American Journal of Research Communication, 1(10) 254–279. [Online]. Available at: http://www.usa-journals.com/wp\ content/uploads/2013/09/Agber2_Vol110.pdf
Agyekum, B. O., & Ossom, S. (2015). Awareness and impact of electronic journals usage by faculty members and lecturers in Kumasi Polytechnic, Ghana. Information and knowledge management, 5(1), 9-17
Ajegbomogun, F.O. (2007). Impediments to harnessing electronic journal on the internet in developing countries: A Nigeria case study. Library hi-tech. 24(6):27-32
Akpojotor, L. O. (2016). Awareness and usage of electronic information resources among postgraduate students of Library and Information Science in Southern Nigeria, Library Philosophy and Practice (e-journal). Available at https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/libphilprac/1408.
Aladeniyi, F. R. (2017).The use of e-journals by academic staff of Rufus Giwa Polytechnic, Owo, Ondo State, Nigeria. International Journal of Library and Information Science, 9(5), 37-43
Ani, O. E., Ngulube, P.,& Onyancha, B. (2015). Perceived effects of accessibility and utilisation of electronic resources on productivity of academic staff of selected Nigerian universities. Sage. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244015607582
Anywhere, B. K., & Paulina, A.A (2018). Accessibility and postgraduate students' use of electronic resources in the University of Cape Coast. Research Journal of Library and Information Science, 2(1), 9-14
Asemi, A. & Riyahiniya, N (2007), “Awareness and Use of Digital Resources in the Libraries of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences of Iran”, TheElectronic Library 35(3)
Bansode, S.Y. (2013). Use and Impact of Electronic Journals on the Users of University of Pune, India. Library philosophy and practice (e-journal).Available at https://digital.commons.unl.ed/libphilprac/347
Bofong, U. I. (2003). Students’ write-up in the polytechnics: Issues arising. Part 1
Boakye, E., Martin-Yeboah, E., & Fynn, K. P. (2015). Access and use of electronic journals by the academic staff of Garden City University College, Kumasi. A paper presented at a Seminar and Annual General Meeting (AGM) of the Ghana Library Association (GLA), November 2015, La-Accra: Ghana International Trade Fair Centre
Chirra, R., & Madhusudhan, M. (2009). Use of electronic journals by doctoral research scholars of Goa University, India. Library Hi Tech News, (10), 12-15.
Cook, C. B., & Jones, S. L. (2000). Electronic journals: Are they a paradigm shift? Available at http://www.nursingworld.ng/ojin/topicII/tpcII_I.htm
Israel, O. & Edesiriu, O. (2017). Undergraduates’ Computer Skills and the Use of Online Information Resources: A Case Study of Library and Information Science Students of Delta State University, Nigeria. International Journal of Academic Library and Information Science. Vol. 4(3), pp. 87-93
Jagboro, K. O. (2003). A study of Internet usage in Nigerian universities: A case study of Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile – Ife, Nigeria. First Monday, 8(2). . Available at http://Firstmonday.Org/Issues/Issue8_2/Jagboro/Index.html
Katabalwa, A.S. & Underwood, P.G (2017) PERii electronic journals: Assessing access and use by postgraduate students in the School of Education at the University of Dar es Salaam. University of Dar es Salaam Journal 12(1), 146-162
Kling, R. & Callahan, E. (2003). Electronic journals, the internet, and scholarly communication. Annual Review of Information Science and Technology 38: 127-177
Lwoga, E. T., Chimwaza, G., Aronson, B., & Vent, O.(2007). Building science information fluency in African Universities: How libraries and researchers are benefiting from improved access to science scholarship, Available at http://www.ifla.org/iv/ifla73/index.htm.
Madhusundhan, M. (2010). Use of electronic resources by scholars of Kurukshetra University. The electronic library, 28(4), 492-506.
Madondo, T., Sithole N., & Chisita, C.T. (2017). Use of electronic information resources by undergraduate students in the Faculty of Management and Administration at Africa University, Mutare Zimbabwe. Asian Research Journal of Arts& Social Sciences 2(2):1-12
Moahi, K. H. (2002). Issues of just-in-time (access) vs. just-in-case (ownership) for libraries in developing countries: Lessons to be learnt from developed countries, Library Review, 51(7), 341-349
Maxymuk, J. (2004). Electronic journals redux: The bottom line: Managing library finances. 17(2), 72-74.
Naick, B. R.D. & Bachalla N. (2016). Application of Digital Forensics in Digital Libraries. International Journal of Library & Information Science (IJLIS). Vol. 5(2), pp. 89–94.
Oduwole, A. A, & Akpati, C. B. (2003). Accessibility and retrieval of electronic information at University of Agriculture Library, Abeokuta, Nigeria. Library Review .52(2), 228-233
Okoye, M. O., & Ejikeme, A. N. (2011). Open access, institutional repositories and scholarly publishing: The role of librarians in South-East Nigeria. Library Philosophy and Practice. Available at https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/libphilprac/612
Otu, B.O, Asante E & Martin OO (2015). Awareness and Utilization of E-Journals by Faculty: Evidence from Koforidug Polytechnic, Ghana. International Journal on New Trends in Education and their Implications 6(4):56-65
Panda, K. C., & Mohanta, R. (2008). Role of e-resources in information retrieval. In: Lal, C. (ed.). Information literacy in the digital age. New Delhi: Ess Pub, 88-101.
Rao, M. K. (2001). Scholarly communication and electronic journals: Issues and prospects for academic and research libraries, Library Review, 50(4):169-175
Rosenberg, D., & Raseroka, K. (2000). Library incomes: Survey of African University Libraries in the SCANUL-ECS region. A paper presented at the 3rd Standing Conference of African National and University Libraries in Eastern, Central and Southern Africa, 10-11 April
Salau, S. A., & Gama, U. G. (2015). Access to and use of electronic journals in selected federal university libraries in the Federal Capital Territory and North Central Zone of Nigeria. African Journal of Library, Archives & Information Science. , 25(2), 161-171
Singh, K. P., & Bebi, M. S. (2012). Use of e-journals by agricultural scientists: A case study of the ICAR libraries in Delhi. Library HERALD, 50(2), 169-179
Shuling, W. (2007). Investigation and analysis of current use of electronic resources in university libraries. Library Management, 28(1-2), 72-88.
Tobia, R.C. & Hunnicutt, S.C. (2008). Print journals in the electronic Library: what is happening to them? Journal of Electronic Resources in Medical Libraries, 5:161-170
Vasishta S., & Naviiyoti, D. R. (2011). Trends in the use of e-journals: A case Study of PEC University of Technology Chandigarh, Library Philosophy and Practice. Available at https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/libphilprac/656.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License which allows users to read, copy, distribute and make derivative works from the material, as long as the author of the original work is cited properly.